Observing the Russia-Ukraine conflict through the lens of alternative data
Macro Insight
QuantCube analyzes public sentiment towards the conflict for the US, Russia and China
QuantCube is monitoring the impact of the Russia-Ukraine crisis on the global economy in real-time using our macroeconomic indicators for variables such as Inflation and international trade. After the war broke out on February 24, these indicators recorded significant changes in direction, suggesting an imminent impact on global economic growth.
Using our proprietary technologies for NLP (Natural Language Processing), QuantCube is also analysing trends in public sentiment towards the conflict, including economic anxiety and people’s inclination for leaving their home country. We’ve observed the effect of the Russia-Ukraine crisis in three major countries: the US, Russia and China.
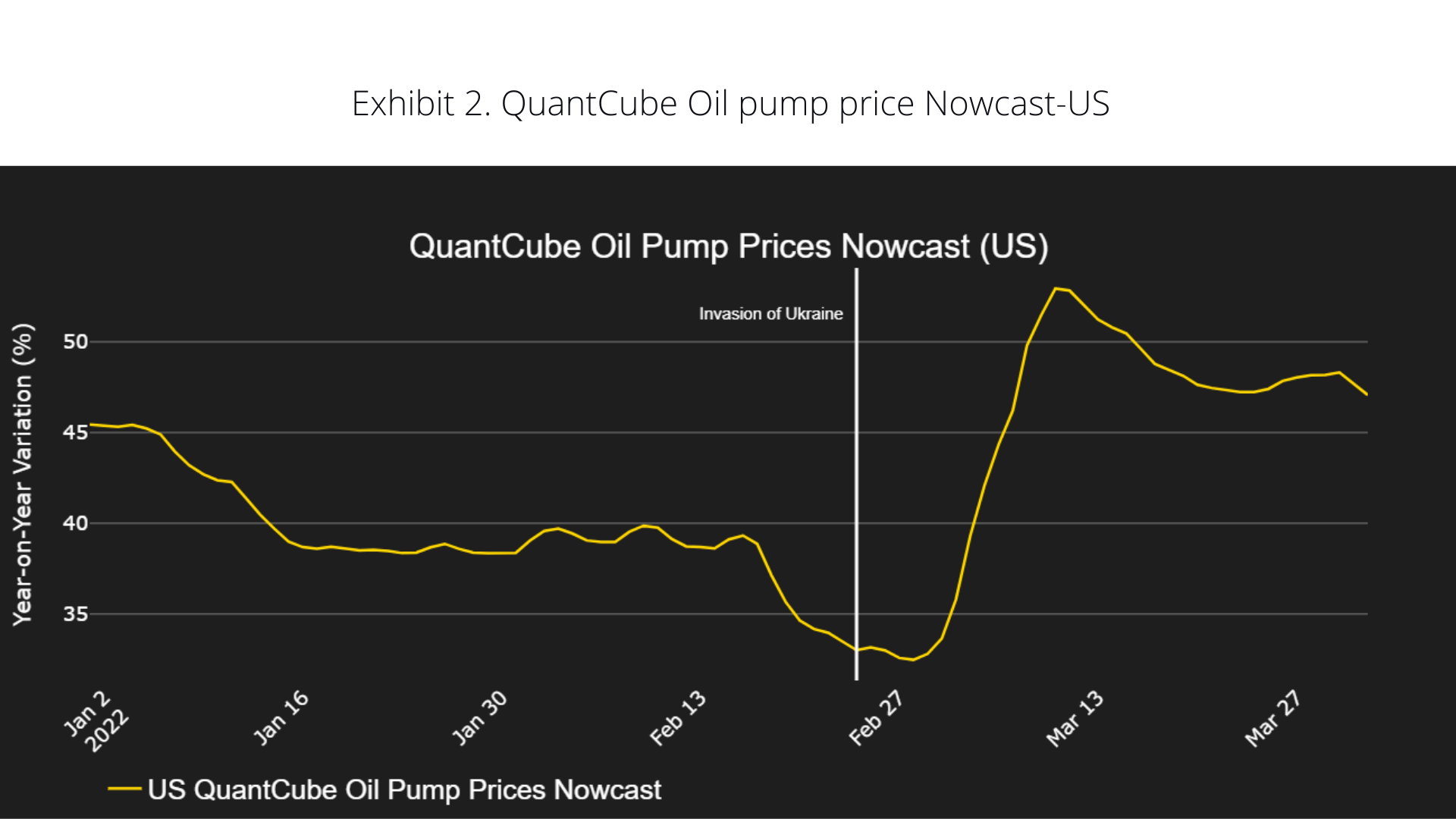
US - Sharp increase in US oil pump prices
Although the Russia-Ukraine conflict is geographically distant, it is causing ripple effects in the US. Exhibit 1 shows that the QuantCube US CPI Indicator has been rising for the last several months, mainly due to increasing commodity prices. The conflict led to shortages in energy supplies and restricted shipments for certain commodities such as metals. This fuelled existing inflationary pressure. The impact of the conflict is particularly significant if we look at the US oil pump price variation (Exhibit 2). The US oil pump price is a sub-component of the QuantCube CPI Indicator for the US. As Russia is one of the world’s largest oil exporters, the economic uncertainty generated by the conflict and the sanctions imposed on Russia caused turmoil in the US oil market. A few days after the conflict started, US oil pump prices rose sharply. In the last two weeks, we observe a slight decrease in oil pump prices, although these remain high and well above the levels of last year, recording a 48% increase.
In Exhibit 3 we observe public anxiety levels in the US using the QuantCube Economic Anxiety Sentiment Indicator. It seems that the concern caused by the conflict and rising cost of living pushed up anxiety levels significantly. The QuantCube US Economic Anxiety Sentiment Indicator rose sharply in March 2022, reaching a level similar to October 2021 when the US experienced a significant supply chain crisis. After the initial shock of the war, the indicator seems to be decreasing and going back to pre-war levels.
Russia - Large scale sanctions starting to bite
We observe that the conflict and the massive sanctions imposed by western countries have started to affect the Russian economy. By using AIS (Automatic Identification System) data that tracks the movement of shipping vessels, QuantCube examines how the crisis is affecting Russian and international trade.
Since the beginning of the conflict, we note a significant drop in the import-export activity at northern-Russian ports, which are mainly used for trade between Russia and northern-European countries. In the meantime, maritime flows from Russian warm-water ports to Turkey and the Middle East are relatively unchanged so far. The flow of shipments from Vladivostok seems to vary by destination countries. We also observe a decrease in trade flows with Japan and South Korea, while there is a slight rise in flows with China.
Due to the significant sanctions imposed globally, Russia and the Russian people are becoming more isolated. According to the QuantCube Russia Economic Anxiety Sentiment Indicator (Exhibit 5), economic anxiety levels experienced by Russian people jumped significantly in March 2022, a 250% increase compared to the level recorded in January 2022.
QuantCube also measures people’s inclination for leaving their home country with its Emigration Indicator. As Exhibit 6 shows, the Quant Cube Emigration Indicator skyrocketed at the end of February. This suggests that heightened fear and uncertainty about their future are driving Russian people to consider leaving their home country. However, similar to the US, both emigration tendencies and economic anxiety started to level off after the initial rise.
China - A complex relationship with Russia
Our data suggests that trade flows between Russia and China have increased since the start of the conflict, which suggests that Russia is trying to strengthen its relationship with China to offset the lack of trade with western countries. China is the only major economy that has not explicitly condemned Russia’s military actions against Ukraine. In addition, they haven’t applied any sanctions against Russia so far. In order to gain deeper insight into public opinion for China’s stance, QuantCube carried out a sentiment analysis of global newspaper articles on the Top 20 Chinese leaders. As demonstrated in Exhibit 7, global sentiment towards these leaders was stable until it dropped sharply at the start of the Russia-Ukraine conflict. This suggests that public opinion of the Chinese administration and its neutral stance toward the conflict was negative. At the same time, we can see a sudden increase in the news volume related to Chinese leaders, suggesting that the global media was closely following the Chinese government’s actions.
Even though Beijing declared China’s neutral stance for the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, Chinese state-owned media continues to spread Kremlin propaganda ensuring that its own media remains pro-Russian. Based on social media analysis, QuantCube developed the Pro-Russian Sentiment Indicator and Pro-Ukraine Sentiment Indicator as shown in Exhibit 8. Interestingly, Pro-Russian sentiment shot up at the start of the conflict while the Pro-Ukraine sentiment had only a moderate upward tick. This indicates the complex nature of China’s relationship with Russia. When we look at the QuantCube Economic Anxiety Sentiment Indicator for China, the anxiety levels experienced by the public in China rose sharply in March as Exhibit 9 indicates.
However, these dropped sharply again in the following few days. This is most likely due to the Chinese government’s initiative to set a ceiling on energy price hikes. In other words, Chinese people are shielded from an unlimited increase in the cost of living. China also signed several deals recently with Russia to secure continuous energy supplies. This too should help curb the impact of higher energy prices on the Chinese economy.
About QuantCube Indicators
QuantCube Economic Anxiety Sentiment Indicator: the indicator measures the level of concern related to the state of the economy. Based on social media, it provides insights into the general public’s opinion towards global and/or local events with potential negative economic impact.
QuantCube Pro-Russia and Pro-Ukraine Indicators: using social media, the indicators capture the local population’s sentiment towards Russia or Ukraine.
QuantCube Emigration Indicator: using social media, the indicator measures the local population’s interest to emigrate and settle permanently in another country.
QuantCube Top 20 Chinese Leaders’ Global Reputation Indicator: this indicator is a sentiment index on Chinese leaders based on the analysis of global newspaper articles.
It reflects the perception of the world's media on a list of Chinese leaders and therefore on their actions.